What is Obesity & Severe Obesity?
Obesity is a treatable disease that is a worldwide health concern associated with having an excess amount of body fat. It is caused by genetic and environmental factors and can be difficult to control through dieting alone. Obesity is diagnosed by a healthcare provider and is classified as having a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or greater. Nearly 40 percent of Americans have obesity.
Obesity Is
- A disease.
- A worldwide health concern.
- Caused by many factors.
- Treatable and manageable.
Obesity Is Not
- Your fault.
- Yours to manage alone.
- Just about food.
- Cured by a miracle treatment.
Body mass index (BMI)
 Body fat is hard to measure directly. So it is often measured by body mass index (BMI). BMI measures weight related to height. It is a common way to measure body fat and is one tool healthcare providers use when talking about weight.
Body fat is hard to measure directly. So it is often measured by body mass index (BMI). BMI measures weight related to height. It is a common way to measure body fat and is one tool healthcare providers use when talking about weight.
To find your BMI, please see the BMI chart here.
BMI is not a percentage of body fat. BMI is only part of a diagnosis of obesity. Ask your healthcare provider for other ways of determining obesity.
How Weight is Categorized
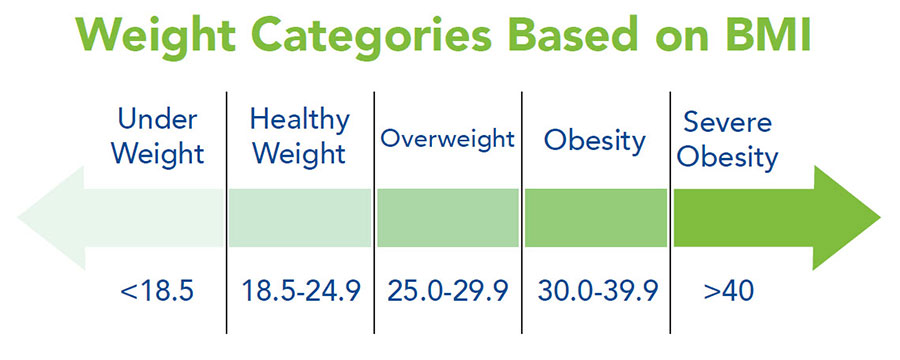
Overweight
Having a BMI in the overweight range (25.0 29.9) is a health concern. Excess weight is hard on your body. It can lead to other health problems including obesity. People who have a BMI in the overweight range and have other health problems (such as type 2 diabetes or heart disease) need to see their healthcare provider for treatment options.
Obesity
Obesity is a disease where a person’s weight is in an unhealthy range (BMI of 30.0-39.9). It is a disease that can lead to other health problems. Talk with your healthcare provider to better understand and treat obesity.
Severe Obesity
Someone who is more than 100 pounds over their healthy body weight (BMI greater than 40) has severe obesity. Severe obesity has the highest risk of other health problems. People with severe obesity need to see their healthcare provider for treatment options.
Causes of Obesity
Better understanding the causes of obesity can help you better treat obesity. Talk with your healthcare provider about your daily habits, medical history and family medical history to determine the best treatment plan for you.
- Obesity is a complicated disease.
- Obesity has more than one cause.
- Obesity is not just about food.
- Obesity is not someone’s fault
Psychological Factors
- Weight management can be challenging if troubled by stress and other concerns.
- You need to work on these issues to be successful with your weight management.
Energy In/Energy Out
- An imbalance of calories in and calories burned may cause weight gain.
- Long daily commutes and desk jobs make it harder to get physical activity.
- Not all communities have safe spaces to run, bike or walk.
- Small bouts of increased physical activity throughout the day can be beneficial.
Sleep Deprivation
- Some studies show a link between how much people sleep and how much people weigh.
- In general, people who do not get enough sleep may weigh more than people who do.
Appetite Signals/Hormones
- Your body has hormones (chemicals in your body that control function and activity of tissues and organs) that help let you know if you are hungry or full..
- The hormones that signal hunger and fullness do not always work correctly in people with obesity.
Genetic Factors
- Genes in your body can determine if you are more likely to have obesity.
- Having these genes is not a reason to give up on losing weight. Weight-loss as small as 5 percent can improve your overall health.
Prescription Medications
- Some prescription medications can cause weight gain of up to several pounds each month.
- Do not stop taking medications you think might be causing weight gain, but speak with your healthcare provider about other medication options.
Environmental Factors
- We are surrounded by television ads, billboards and images that promote the consumption of foods and beverages that are high in calories and fat.
- Some neighborhoods have little or no access to fresh, healthy foods.
What Are the Risks Associated with Obesity?
Excess weight can be hard on your whole body. More than 50 health problems are related to excess weight and obesity. These health problems are diseases and conditions that can decrease your quality of life and are commonly called obesity-related conditions. It is important to talk with your healthcare provider about these conditions.
- Not everyone with obesity will develop every obesity-related condition.
- The more weight you carry, the more likely you are to develop obesity-related conditions.
- Finding and treating health conditions early is best for your overall health.
- Weight-loss as small as 5-10% can reduce the effects of obesity-related conditions.
For more information on obesity-related conditions, please click here.
Obesity is Linked to More Than 50 Disorders
 The Most Common Obesity-Related Conditions Include:
The Most Common Obesity-Related Conditions Include:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Type 2 diabetes
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Gallbladder disease
- Osteoarthritis
- Sleep apnea
- Respiratory problems
- Fatty Liver disease
- Venous disease
- Acid reflux
- Menstrual irregularities and infertility
13 Types of Obesity-Related Cancers Include:
- Meningioma (brain tissue and spinal cord)
- Thyroid
- Adenocarcinoma of the esophagus
- Multiple myeloma (blood cells)
- Breast (post-menopausal women)
- Liver
- Kidney
- Gallbladder
- Upper stomach
- Pancreatic
- Colon and rectal
- Uterine
- Ovarian
What are the societal effects of obesity & severe obesity?
Obesity can impact your life in ways beyond physical health. Our culture focuses on body size and appearance. When combined with misunderstanding and negative attitudes by others, discrimination and bias occurs. As part of daily life, this bias and discrimination can lead to a decreased quality of life and emotional pain.
Effects at Home & Among Friends
Family and friends are not always supportive. They may not understand the causes and risks of obesity. They might also fail to support you in your decision to manage your weight.
Effects at Work
Employees with obesity are often viewed as lazy or less competent. Sometimes they are seen as undisciplined, less ambitious or less productive. They also face lower wages and are less likely to be hired or promoted.
Effects in Healthcare Settings
Patients with obesity and severe obesity can face discrimination in healthcare settings. This can lead to much greater health problems. People faced with this situation often delay seeing their healthcare provider. Some may cancel appointments or not seek treatment at all.
What Treatment Options Should Be Considered?
Treatment plans are made for each individual. Your plan will likely not be the same as for others sitting in the waiting room. But early treatment is best for everyone. Always talk with your healthcare provider before starting a weight management program. Many treatment options are available and a combination is often used to manage obesity.
Your healthcare providers play a major role in your weight management journey. They help you manage your weight and guide you with tools, resources and support. This partnership can make all the difference. You do not need to manage your weight alone. Visit Obesity Care Providers powered by the OAC to find an Obesity Care Provider in your area: ObesityCareProviders.com
Lifestyle Modifications
Your everyday choices are your behaviors. They include everything from sleeping to what you have for lunch and if you take the stairs or the elevator. They fit together like puzzle pieces to form your lifestyle. A healthy lifestyle can look like this:
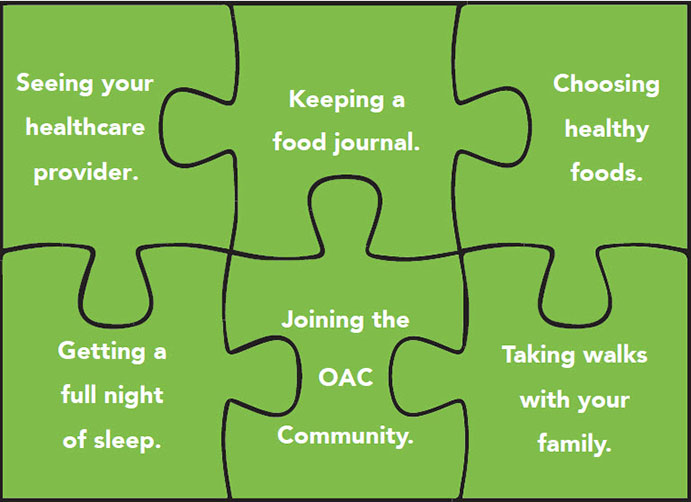
Focusing on manageable modifications to improve your health is the goal. Do not become discouraged. Healthy is a lifestyle, not a size. Weight-loss as small as 5-10 percent can improve your overall health. It will take time and you may face set-backs, but the health benefits are significant.
Physical Activity Modifications
Physical activity is key when managing obesity. It is best to start simple and keep it manageable. Take a walk around the block after dinner or park far away from the store. These are easy ways to make physical activity part of your day. Make sure to speak with your healthcare provider before starting any exercise program.
When making an exercise and physical activity plan, remember to:
- Make it simple.
- Make it realistic.
- Make it happen.
- Make it fun.
Nutrition Modifications
Changing your eating habits can be hard. We are surrounded by convenience foods high in fat and calories and low in nutritional value. Knowing which foods to pick for a healthy diet can be hard as well. There are options to help. Non-clinical and clinical (medical) weight management options are ways to get help and learn more about nutrition and healthy eating.
Weight Management Options
Non-Clinical Weight Management Options
Non-clinical weight management programs can be self-managed. They can also be offered by someone other than a healthcare provider. These programs range from books and websites to chain weight-loss programs or support groups. Finding the right option for you is important. Take time to read about several and talk about them with your healthcare provider. The success of any option takes a commitment to your goal of improving your health.
People with severe obesity have greater health risks. Clinical weight management programs and bariatric surgery are options for treatment. Talk with your healthcare provider about these options.
Clinical Weight Management Options
A physician who specializes in obesity medicine (ABOM Certified*) can offer you a clinical weight management program. Additional healthcare providers may be part of your program. Nurses, nurse practitioners and physician assistants may help with routine monitoring. Registered dietitians may give you healthy eating tips and menus. Psychologists may talk with you about stress in your life and how your eating is impacted. These programs focus a great deal on lifestyle changes, but might also include FDA- approved medicines for chronic weight management. Routine visits with all team providers is important for success.

People with severe obesity have greater health risks. Clinical weight management programs and bariatric surgery are options for treatment. Talk with your healthcare provider about these options.
Medical Weight Management & Bariatric Surgery Options
Some prescription medications help with weight-loss. Your healthcare provider may want them in your treatment plan. Your provider will tell you about the risks and benefits. These prescription medications work in combination with lifestyle modifications. Currently, there are several FDA-approved medications for chronic weight management.
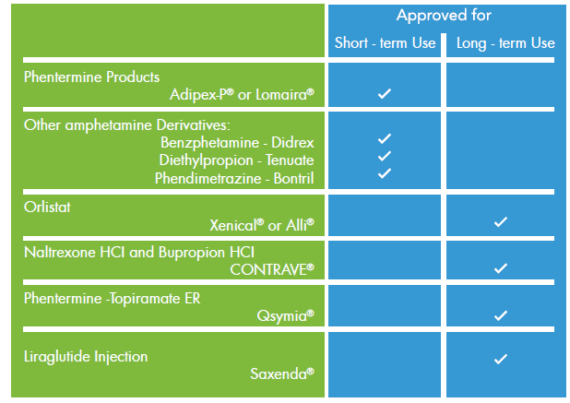
Chronic Weight Management Medications:
Some healthcare providers may use prescription medicines usually given to treat other diseases for the treatment of obesity.
Bariatric Surgery and Devices
Bariatric surgery is a safe and effective procedure to treat obesity and severe obesity. Surgery is primarily used to treat patients with a BMI greater than 35 when you have at least one obesity-related condition such as type 2 diabetes or high blood pressure or a BMI greater than 40 without obesity-related conditions. With some surgeries or devices, procedures may be performed on those with a BMI as low as 30.
Bariatric surgery is also commonly called “the treatment of obesity and severe obesity surgery.” Please note for the purpose of this brochure, we’ll refer to it as “bariatric surgery.” Bariatric surgery helps in weight-loss by limiting the amount of food your stomach can hold.
Device procedures for weight-loss can limit the amount of food the stomach can hold, make you feel full with smaller amounts of food or by aspirating food following meals. Bariatric devices are not a permanent change and are removed at a time determined by your healthcare provider.
Surgery and device procedures are not miracle cures. Following these procedures, you must make lifestyle modifications including healthy eating and increased physical activity. You will need a support system, and be willing to follow all directions from your healthcare provider. Your healthcare provider will help you decide if one of these procedures is part of your treatment. Several types of bariatric surgery and device implants are available.
Be sure to talk with your provider about all risks and any FDA warnings before any medical procedure.
Bariatric Surgery Options:
- Sleeve Gastrectomy
- Roux en-Y Gastric Bypass
- Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch
Bariatric Device Options:
- Adjustable Gastric Banding (LAP-BAND )
- Aspire Assist
- Gastric Balloon
- Neuromodulation (VBLOC )
Deciding to have surgery is not simple, but you do not make the decision alone. Your surgeon will help you decide. You need to balance the health concerns of severe obesity with the potential risks of surgery. This treatment option is a tool that is part of a long-term plan to lose and manage your weight. Overall lifestyle changes are key for maintaining a healthy quality of life after surgery.
If bariatric surgery is an option, you will likely be sent to see a psychologist. It is a normal part of surgery preparation. Together, the two of you will work to be ready for surgery. A team of providers will be part of your care following surgery. The team will likely include a dietitian, exercise therapist and psychologist. They will get to know you and are part of your support system.
To learn more about bariatric surgery, visit the Obesity Treatments section of the OAC website here.
Gaining Access to Treatment with Your Insurance Provider
People affected by obesity count on their insurance provider. They help you have safe and effective medical treatment. Working with your provider is not always easy. You can experience problems and delays. The most common problem is repeated claim denials. All of this can become physically and emotionally draining.
The OAC designed Working with Your Insurance Provider: A Guide to Seeking Weight-loss Surgery to help. It focuses on coverage for bariatric surgery. To view this brochure, please click here.
To download a PDF version of this brochure, click here.